Introduction to the gut-brain connection
The human body is an incredibly complex system, and it’s only in recent years that we’ve begun to understand the intricate connections between our organs and systems. One of the most fascinating of these is the gut-brain connection, which refers to the bidirectional communication between the gut and the brain. This connection is the reason why gut health is crucial for mental health and why an imbalance in the gut microbiome can lead to anxiety and depression.
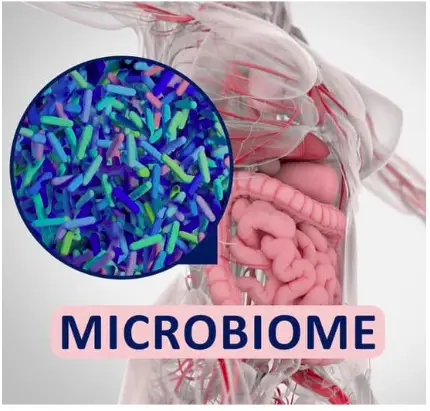
What is gut health and why is it important for mental health?
Gut health refers to the balance of microorganisms in the gut, which includes bacteria, viruses, and fungi. These microorganisms play a crucial role in the body’s immune system, digestion, and overall health. When the balance of microorganisms in the gut is disrupted, it can lead to a range of health problems, including mental health issues.
Research has shown that the gut is often referred to as the second brain, and it’s easy to see why. The gut contains over 100 million neurons, which communicate with the brain via the vagus nerve. This communication plays a vital role in regulating mood, behavior, and cognitive function.
The gut microbiome and its impact on mental health
The gut microbiome refers to the collection of microorganisms that live in the gut. This microbiome plays a crucial role in maintaining gut health, and research has shown that it also has a significant impact on mental health. The gut microbiome communicates with the brain via the gut-brain axis, which means that an imbalance in the microbiome can have a direct impact on mental health.
Studies have shown that people with depression and anxiety often have an imbalance in their gut microbiome. This imbalance can lead to inflammation, which is a known contributor to mental health issues. Additionally, an imbalance in the gut microbiome can lead to nutrient deficiencies, which can further contribute to mental health problems.
The link between gut health and anxiety
Anxiety is a common mental health disorder, affecting millions of people worldwide. While the causes of anxiety are complex and varied, research has shown that gut health plays a significant role in its development. Studies have found that people with anxiety often have an imbalance in their gut microbiome, which can lead to an increase in inflammation and a decrease in the production of neurotransmitters such as serotonin.
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in regulating mood and behavior, and an imbalance in its production can lead to anxiety and depression. Additionally, the gut microbiome is responsible for the production of GABA, a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in reducing anxiety.
The link between gut health and depression
Depression is another common mental health disorder that is often linked to gut health. Like anxiety, depression is a complex condition with numerous contributing factors. However, research has shown that an imbalance in the gut microbiome can play a significant role in its development.
Studies have found that people with depression often have a lower diversity of gut bacteria, which can lead to inflammation and a decrease in the production of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine. Additionally, an imbalance in the gut microbiome can lead to an increase in the production of stress hormones such as cortisol, which can further contribute to depression.
The role of diet in gut health and mental health
Diet plays a vital role in maintaining gut health and can have a significant impact on mental health. A diet that is high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can lead to an imbalance in the gut microbiome and an increase in inflammation. On the other hand, a diet that is rich in whole foods, fiber, and healthy fats can help to promote a healthy gut microbiome and reduce inflammation.

Gut-friendly foods to improve mental health
The following foods are excellent for promoting gut health and improving mental health:
- Fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, and kimchi, which are rich in probiotics
- Prebiotic foods such as garlic, onions, and asparagus, which help to feed the good bacteria in the gut
- Fiber-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, which help to promote a healthy gut microbiome
- Omega-3 rich foods such as fatty fish, nuts, and seeds, which can help to reduce inflammation and promote healthy brain function
Probiotics and their impact on mental health
Probiotics are live microorganisms that can help to promote a healthy gut microbiome. Studies have shown that taking probiotics can help to reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety. Additionally, probiotics can help to reduce inflammation, which is a known contributor to mental health issues.
Lifestyle changes to improve gut health and mental health
In addition to diet and probiotics, there are several lifestyle changes that people can make to promote gut health and improve mental health. These include:
- Reducing stress through practices such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing
- Getting regular exercise, which can help to reduce inflammation and promote a healthy gut microbiome
- Getting enough sleep, which is crucial for both gut health and mental health
- Avoiding antibiotics unless absolutely necessary, as they can disrupt the gut microbiome
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, which can disrupt gut health
Conclusion: Taking care of your gut for better mental health
In conclusion, the gut-brain connection is a fascinating and complex system that plays a crucial role in mental health. Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome through diet, probiotics, and lifestyle changes can help to reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression and promote better overall mental health. By taking care of your gut, you can take care of your mind. If you’re struggling with anxiety or depression, take a look at your gut health. Making changes to your diet and lifestyle can have a significant impact on your mental health. Additionally, consider taking a probiotic supplement to help promote a healthy gut microbiome. Remember, taking care of your gut is crucial for taking care of your mind.